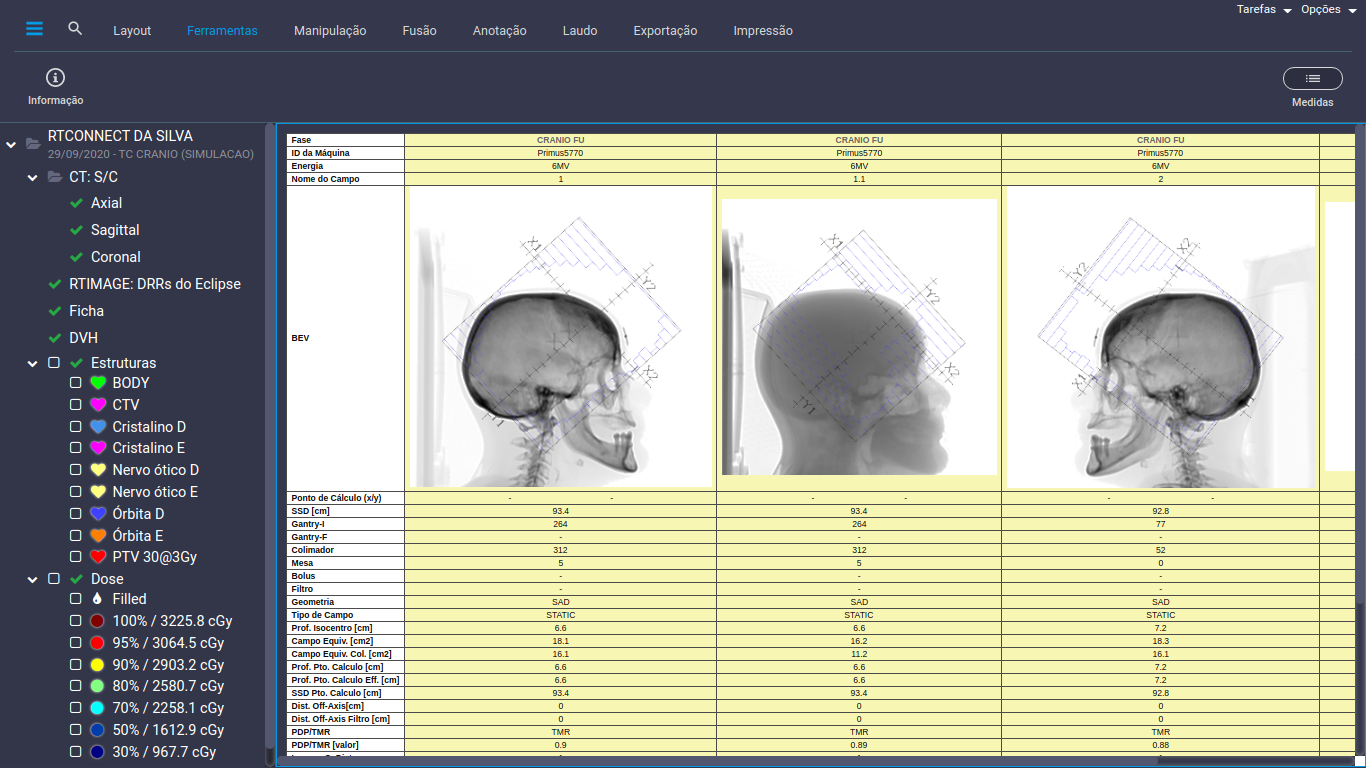
Radiation therapy is an important part of cancer treatment, delivering high doses of radiation to specific areas of the body to destroy cancer cells. However, the success of the treatment relies on accurate and precise calculations of the amount of radiation required, known as monitor units. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has recently reported that nearly 60% of reported errors in radiation therapy treatment planning involved a lack of appropriate independent secondary verification.
Secondary Verification in Radiation Therapy
The secondary verification of the treatment plan and dose calculation is a critical step in ensuring the accuracy of the monitor unit calculations. This process involves reviewing the initial calculation to identify any errors or inaccuracies and making any necessary adjustments to ensure the correct dose of radiation is delivered to the target area. The secondary verification should be performed independently, by a different professional than the one who performed the initial calculation, to ensure that the process is objective and unbiased.
A lack of independent secondary verification can result in incorrect monitor unit calculations, leading to suboptimal treatment
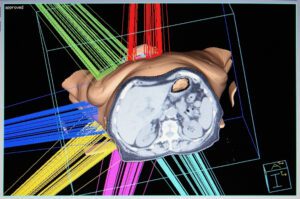
TPS
outcomes and an increased risk of side effects. Furthermore, the delivery of a higher dose of radiation than required can result in long-term damage to the surrounding healthy tissue, while a lower dose can result in cancer cells surviving and potentially leading to recurrence.
To avoid these risks, it is essential that healthcare professionals adopt a rigorous quality assurance process that includes independent secondary verification of the treatment plan and dose calculation. This process should be performed by trained and qualified professionals, using the latest technology and software solutions to ensure accuracy and consistency.