Introduction to Patient Positioning in Radiotherapy
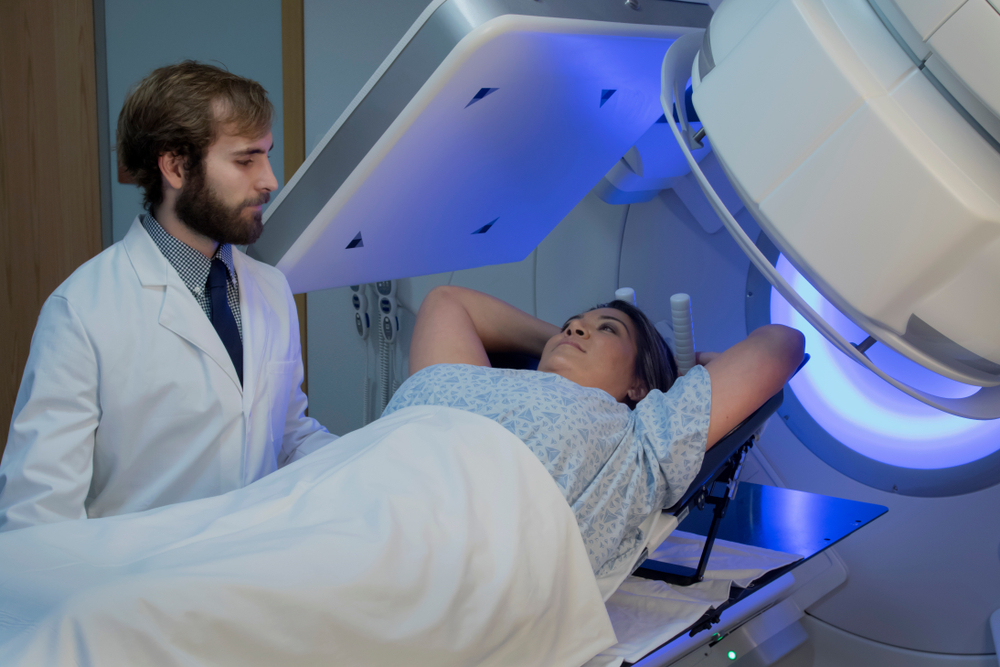
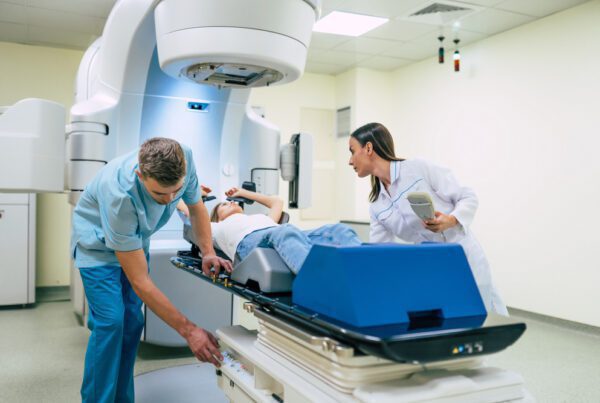
Patient positioning is a critical aspect of radiation therapy, as it ensures the accurate delivery of radiation to the tumor site while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Proper positioning also enhances patient comfort and safety throughout the treatment process. In this blog post, we will explore the factors that affect patient positioning, the techniques and tools used to achieve accuracy, and the challenges faced by healthcare professionals.
Factors Affecting Patient Positioning
Several factors influence patient positioning in radiotherapy:
Tumor location: The position of the tumor within the body plays a significant role in determining the optimal patient position.
Patient anatomy: Each patient’s unique anatomy must be considered to ensure the most effective and comfortable positioning.
Treatment planning: The radiation oncologist’s treatment plan, including the dose and duration of radiation, affects patient positioning.
Equipment limitations: The radiotherapy equipment used may impose constraints on patient positioning.
Techniques and Tools for Accurate Patient Positioning
Various techniques and tools are utilized to achieve accurate patient positioning in radiotherapy:
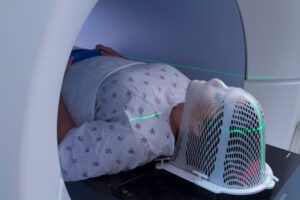
Example of positioning accessory
Immobilization devices: Devices like thermoplastic masks, vacuum cushions, and breast boards help stabilize the patient and maintain a consistent position during treatment.
Lasers and room-based markers: Lasers and markers guide healthcare professionals in aligning the patient with the radiation source accurately.
Customized positioning aids: Pillows, cushions, and supports tailored to the patient’s anatomy can improve both comfort and positioning accuracy.
The Role of Imaging in Patient Positioning
Imaging plays a vital role in patient positioning, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the tumor and surrounding tissues:
CT scans: CT scans are often used in treatment planning, providing detailed images of the tumor and patient anatomy.
Cone-beam CT (CBCT): This imaging technique is performed using the linear accelerator, helping to verify patient positioning immediately before treatment.
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used in specific cases to gather more information about the tumor and surrounding tissues.
Addressing Challenges in Patient Positioning
Patient positioning in radiotherapy can present various challenges, including:
Reproducibility: Ensuring consistent patient positioning across multiple treatment sessions is crucial for treatment effectiveness.
Comfort: Balancing patient comfort with the need for accurate positioning can be a delicate process.
Time constraints: Healthcare professionals must efficiently position patients to minimize overall treatment time.
Collaboration between the patient, radiation oncologist, and therapy team is key to overcoming these challenges and achieving accurate and comfortable patient positioning.
Conclusion
Patient positioning plays a vital role in the success of radiotherapy, impacting treatment accuracy and patient comfort. By understanding the factors that affect positioning and the tools and techniques used to achieve it, healthcare professionals can work together to deliver the best possible outcomes for their patients.
Interested in learning more about radiation therapy essentials? Discover the importance of breast boards in radiotherapy and how they contribute to effective treatment and patient comfort.